Megatron-LM源码系列(三):详解Pipeline模型并行训练实现
在【Megatron-LM源码系列(二):Tensor模型并行和Sequence模型并行训练】基础上增加了Pipeline模型并行训练的介绍,对于Pipeline模型并行思路可参考【详解MegatronLM流水线模型并行训练(Pipeline Parallel)】。pipeline并行中网络是按层的粒度进行纵向切分,在通信组通信上中在pipeline的不同stage中进行横向通信。如下图中2机16卡每个色块就是一个pipeline通信组,训练前向通信的顺序是从左向右。
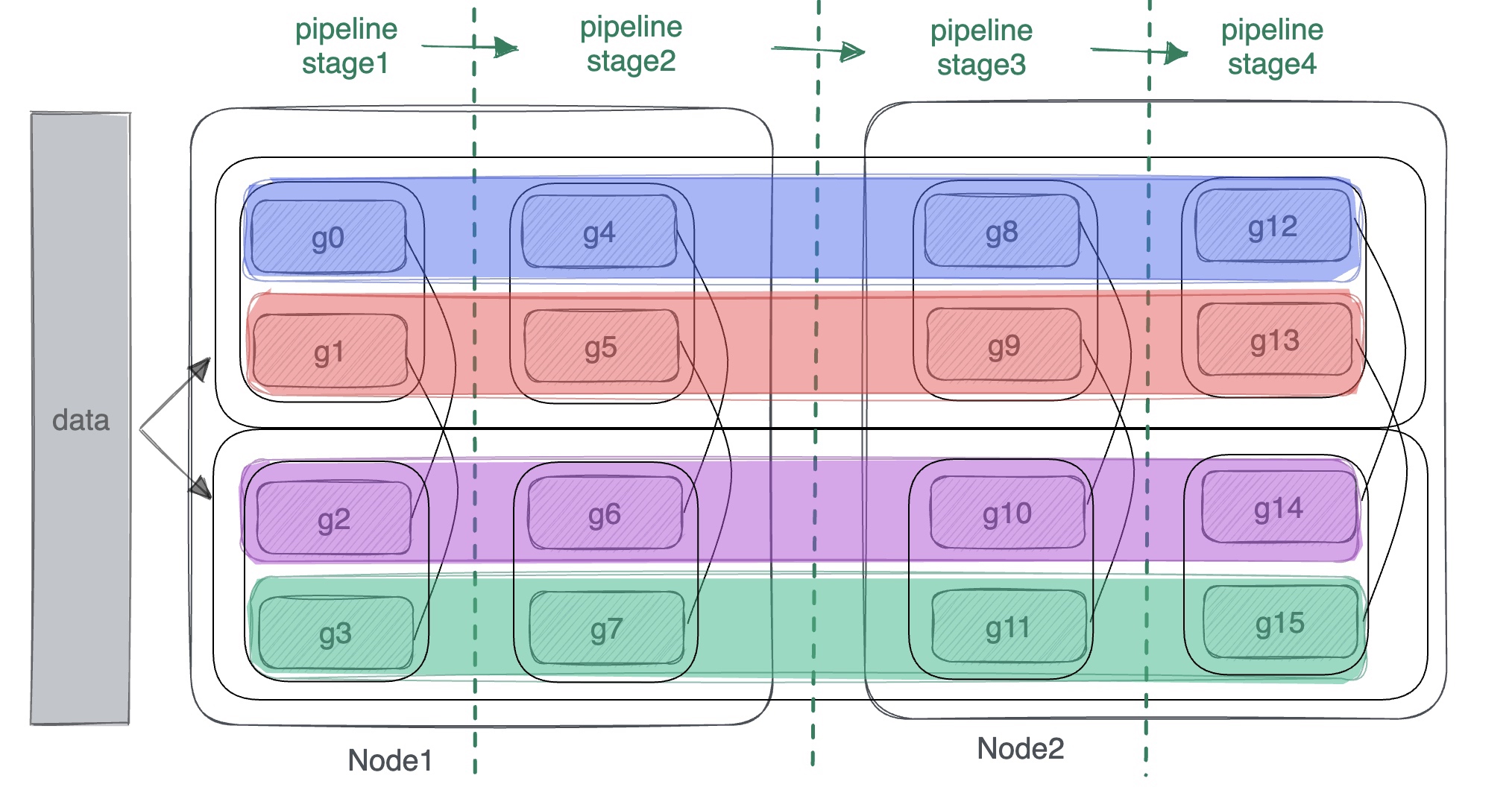
pipeline模型并行训练实现的代码在megatron/core/pipeline_parallel目录下,有两个主要文件,分别是p2p_communication.py和schedules.py。
1. p2p_communication.py
1.1 p2p接口定义
在p2p_communication.py中会用到megatron/core/parallel_state.py中定义的四种函数,分别是
*
get_pipeline_model_parallel_group:获取当前rank所在的pipeline并行通信组
*
get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank:获取所在pipeline并行通信组的当前rank号
*
get_pipeline_model_parallel_prev_rank:获取所在pipeline并行通信组的前一个rank号
*
get_pipeline_model_parallel_next_rank:获取所在pipeline并行通信组的下一个rank号
pipeline模型并行用到的通信都是p2p点对点的,底层对应通信库中的send和recv两个原语。实际使用过程中定义了如下的几个接口:
* recv_forward:
从pipeline并行组的前一个rank获取数据,函数里面会直接调用_communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14def recv_forward(tensor_shape: Shape,
dtype: torch.dtype,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
timers: Callable = None) -> torch.Tensor:
...
input_tensor, _, _ = _communicate(
tensor_send_next=None,
tensor_send_prev=None,
recv_prev=True,
recv_next=False,
tensor_shape=tensor_shape,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
dtype=dtype)
..._communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14def recv_forward(tensor_shape: Shape,
dtype: torch.dtype,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
timers: Callable = None) -> torch.Tensor:
...
input_tensor, _, _ = _communicate(
tensor_send_next=None,
tensor_send_prev=None,
recv_prev=True,
recv_next=False,
tensor_shape=tensor_shape,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
dtype=dtype)
..._communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13def send_forward(output_tensor: torch.Tensor,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
timers: Callable = None) -> None:
...
_communicate(
tensor_send_next=output_tensor,
tensor_send_prev=None,
recv_prev=False,
recv_next=False,
tensor_shape=None,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
dtype=None)
..._communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13def send_backward(input_tensor_grad: torch.Tensor,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
timers: Callable = None) -> None:
...
_communicate(
tensor_send_next=None,
tensor_send_prev=input_tensor_grad,
recv_prev=False,
recv_next=False,
tensor_shape=None,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
dtype=None)
..._communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13def send_backward(input_tensor_grad: torch.Tensor,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
timers: Callable = None) -> None:
...
_communicate(
tensor_send_next=None,
tensor_send_prev=input_tensor_grad,
recv_prev=False,
recv_next=False,
tensor_shape=None,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
dtype=None)
..._communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15def send_backward_recv_forward(input_tensor_grad: torch.Tensor,
tensor_shape: Shape,
dtype: torch.dtype,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
timers: Callable = None) -> torch.Tensor:
...
input_tensor, _, _ = _communicate(
tensor_send_next=None,
tensor_send_prev=input_tensor_grad,
recv_prev=True,
recv_next=False,
tensor_shape=tensor_shape,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
dtype=dtype)
..._communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18def send_backward_recv_backward(input_tensor_grad: torch.Tensor,
recv_next: bool,
tensor_shape: Shape,
dtype: torch.dtype,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
overlap_p2p_comm: bool = False,
timers: Callable = None) -> torch.Tensor:
...
input_tensor, _, wait_handles = _communicate(
tensor_send_next=output_tensor,
tensor_send_prev=None,
recv_prev=recv_prev,
recv_next=False,
tensor_shape=tensor_shape,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
wait_on_reqs=(not overlap_p2p_comm),
dtype=dtype)
..._communicate。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18def send_backward_recv_backward(input_tensor_grad: torch.Tensor,
recv_next: bool,
tensor_shape: Shape,
dtype: torch.dtype,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
overlap_p2p_comm: bool = False,
timers: Callable = None) -> torch.Tensor:
...
_, output_tensor_grad, wait_handles = _communicate(
tensor_send_next=None,
tensor_send_prev=input_tensor_grad,
recv_prev=False,
recv_next=recv_next,
tensor_shape=tensor_shape,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
wait_on_reqs=(not overlap_p2p_comm),
dtype=dtype)
..._communicate。 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19def send_forward_backward_recv_forward_backward(
output_tensor: torch.Tensor,
input_tensor_grad: torch.Tensor,
recv_prev: bool,
recv_next: bool,
tensor_shape: Shape,
dtype: torch.dtype,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
timers: Callable = None) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
...
input_tensor, output_tensor_grad, _ = _communicate(
tensor_send_next=output_tensor,
tensor_send_prev=input_tensor_grad,
recv_prev=recv_prev,
recv_next=recv_next,
tensor_shape=tensor_shape,
batch_p2p_comm=batch_p2p_comm,
dtype=dtype)
...
1.2 _communicate实现
在p2p接口都是直接使用的_communicate函数,_communicate函数定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11def _communicate(*, tensor_send_next: Optional[torch.Tensor],
tensor_send_prev: Optional[torch.Tensor],
recv_prev: bool,
recv_next: bool,
tensor_shape: Shape,
batch_p2p_comm: bool = True,
wait_on_reqs: bool = True,
dtype: Optional[torch.dtype],
variable_seq_lengths: bool = False,
use_ring_exchange_p2p: bool = False,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:batch_isend_irecv,为False的话就改为使用isend和irecv
* wait_on_reqs:
使用isend和irecv的话,每次在请求结束前进行阻塞操作
* dtype:接收tensor的数据类型 *
variable_seq_lengths:当训练过程中sequence的长度不是固定的,则设置为True
*
use_ring_exchange_p2p:使用自定义的ring_exchange kernel,代替torch.distributed.batch_isend_irecv()
在_communicate函数中会先进行接收buffer的初始化操作。
1 | if recv_prev: |
初始化以后调用p2p_func进行数据的接收和发送,这里_batched_p2p_ops调用的是batch_isend_irecv,_p2p_ops调用的是isend和irecv,同时也支持使用torch.distributed.ring_exchange。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17# Send tensors in both the forward and backward directions as appropriate.
if use_ring_exchange_p2p:
def _ring_exchange_wrapper(**kwargs):
torch.distributed.ring_exchange(**kwargs)
return []
p2p_func = _ring_exchange_wrapper
elif batch_p2p_comm:
assert wait_on_reqs
p2p_func = _batched_p2p_ops
else:
p2p_func = _p2p_ops
reqs = p2p_func(tensor_send_prev=tensor_send_prev,
tensor_recv_prev=tensor_recv_prev,
tensor_send_next=tensor_send_next,
tensor_recv_next=tensor_recv_next,
group=get_pipeline_model_parallel_group())
2. schedules.py
2.1 get_forward_backward_func
get_forward_backward_func是训练中用到的入口,用于选择训练用到的前向和反向的方法,对应有三种方式:
1.
forward_backward_no_pipelining:没用使用pipeline并行(也就是没有跨stage的通信)
2.
forward_backward_pipelining_without_interleaving:这是采用的PipeDream-2BW的1F1B的训练
3.
forward_backward_pipelining_with_interleaving:这是在megatron-2论文中提到的基于PipeDream-2BW的改进,在每个卡上支持多个stage。
1 | def get_forward_backward_func(): |
forward_backward_func在实际中的使用(megatron/training.py)如下,在写完forward_step_func前向过程后,使用forward_backward_func进行封装。
1 | forward_backward_func = get_forward_backward_func() |
2.2 forward_backward_no_pipelining
forward_backward_no_pipelining中以microbatch为粒度,先进行前向计算,紧跟着进行反向计算,前n-1个microbatch不会进行同步操作,直到最后一个再进行同步。这个过程中不涉及跨stage的通信,同时也不支持sequence并行。前向计算的loss会存在forward_data_store中返回。
1 | if no_sync_func is None and isinstance(model, torchDDP): |
2.3 forward_backward_pipelining_without_interleaving
实现了non-interleaved的1F1B算法,在最后一个stage返回loss。在执行过程中先进行warmup的microbatch的计算。执行的时候先调用recv_forward从前一个stage获取上一个rank的输出,对于第一个stage是从dataloader获取输入;然后执行forward_step进行当前stage的前向计算;然后通过send_forward把结果输传给下一个stage。
1 | def forward_backward_pipelining_without_interleaving(*,...): |
执行warmup操作后开始进入1F1B的稳定状态,
先进行前向forward_step计算并调用send_forward_recv_backward传给下一个stage。这里forward_step_func是跟每个模型相关的,是在模型初始化定义的。
1 | # Run 1F1B in steady state. |
在1F1B中通过buffer保存前向的输入和输出用于反向的计算,
每次计算的时候会pop出来一组input和output,计算完backward后会通过send_backward_recv_forward把梯度回传给前一个stage:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21# 1. Add input_tensor and output_tensor to end of list.
input_tensors.append(input_tensor)
output_tensors.append(output_tensor)
deallocate_output_tensor(output_tensor[0], deallocate_pipeline_outputs)
# 2. Pop input_tensor and output_tensor from the start of the list for
# the backward pass.
input_tensor = input_tensors.pop(0)
output_tensor = output_tensors.pop(0)
input_tensor_grad = \
backward_step(grad_scaler, input_tensor, output_tensor,
output_tensor_grad, model_type, timers, deallocate_pipeline_outputs)
# 3. 反向结果传递
if last_iteration:
input_tensor = None
send_backward(input_tensor_grad, recv_tensor_shapes, timers=timers)
else:
input_tensor = \
send_backward_recv_forward(
input_tensor_grad, recv_tensor_shapes, dtype, timers=timers)
跟warmup类似,在最后还有一个要等所有backward结束的阶段(cooldown backward passes)
1 | # Run cooldown backward passes. |
最后思考一个问题:在forward_backward_pipelining_without_interleaving中怎么保证后向用到的参数跟前向一样的?这个问题是通过DDP中的取消梯度同步的context函数model.no_sync来解决的。在前N-1个microbatch的backward前只做梯度的累加,只有在最后第N个microbatch完成backward才进行梯度的实际更新。
1 | # Disable async grad reductions |
2.4 forward_backward_pipelining_with_interleaving中的模型构建
forward_backward_pipelining_with_interleaving也是定义在megatron/core/pipeline_parallel/schedules.py。它的实现interleaved 1F1B调度方法的基本思路和forward_backward_pipelining_without_interleaving类似。区别在于要对model模型进行进一步的拆分为多块(chunk)。
回顾下在启用interleaving pipeline的时候,在megatron/core/parallel_state.py中的initialize_model_parallel函数中必须要设置virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size,表示每个device会处理几个stage,例如:对于一个有16层的transformer网络来说,训练配置tensor_model_parallel_size=1, pipeline_model_parallel_size=4, virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size=2,表示模型会被分为4*2=8个stage,每个stage有2个layer,对于一个pipeline通信组的4个gpu
device来说,每个device会处理2个stage。如果virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size不设置为None的情况下,不会启动interleaving。
1 | GPU 0: [1, 2] [9, 10] |
interleaving
pipeline并行对model的分chunk构建,具体通过setup_model_and_optimizer进行构建。
1 | def setup_model_and_optimizer(model_provider_func, |
在setup_model_and_optimizer中会调用megatron/training.py的get_model方法,在get_model方法中会按照设的args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size个数返回一个同等长度的model列表,每一个virtual_pipline会对应一个model。注意这里每个model会被设置virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_rank,即mpu.set_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_rank(i)
1 | def get_model(model_provider_func, model_type=ModelType.encoder_or_decoder, wrap_with_ddp=True): |
在megatron/model/transformer.py文件中的ParallelTransformer函数中有针对流水线并行对model进行按layer层的划分。切分的基本思路是对transformer中的layer列表进行按比例切分为N份,每个rank结点上保存各自的模型(继承自torch.nn.module),每个module中分别有layer_num/N个layer,layer确定是从原始的layer列表中通过计算offset偏移来得到的。
在划分的时候先调用_get_num_layers获得切分后的layer个数:
1
2self.num_layers = _get_num_layers(args, model_type,
layer_type==LayerType.decoder)
在_get_num_layers中这里只分析decoder结构的情况,只有在embedding stage且当前结点rank在通信组中为0的情况下num_layers等于0,否则num_layers等于传入的args.num_layers除以流水线并行度,
比如设置了transformer的layer有8层,pipeline并行度为2,那么这里的self.num_layers的值会被更新为4。
1 | def _get_num_layers(args, model_type, is_decoder=False): |
更新得到切分后的num_layers以后,对于非interleaving的情况中,对于只有decoder结构的模型,offset计算是按rank来算,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class ParallelTransformer(MegatronModule):
"""Transformer class."""
def __init__(...):
......
if args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size is not None:
......
else:
# 对于非interleaving的情况
# Each stage gets a contiguous set of layers.
if args.model_type == ModelType.encoder_and_decoder and \
mpu.get_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size() > 1:
......
else:
# 对于只有decoder结构的模型
offset = mpu.get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank() * self.num_layers
对于interleaving的情况中,self.num_layers需要进一步按args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size切分为更小的块(chunk)。
1 | class ParallelTransformer(MegatronModule): |
在非interleaving的情况下,得到offset后开始实际创建当前rank结点保存的ModuleList,这里的ModuleList中每一层是一个layer,传入的数表示当前layer的编号。比如以num_layer=8, pipeline_stage=2为例,offset是4,对应创建的两个ModuleList,device0中ModuleList是ModuleList(l1,l2,l3,l4),
device1中的是ModuleList(l5,l6,l7,l8)。
1 | class ParallelTransformer(MegatronModule): |
讨论interleaving
offset实现前,先回顾下training.py中对每个device创建model
list过程,如果是interleaving情况下,每个device实际会保存args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size个model,做为一个虚拟组,每个model中只保存原有网络的部分layer。这里的model_provider_func最终会调用到ParallelTransformer的初始化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12def get_model(model_provider_func, ...):
......
model = []
for i in range(args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size):
mpu.set_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_rank(i)
......
this_model = model_provider_func(
pre_process=pre_process,
post_process=post_process
)
this_model.model_type = model_type
model.append(this_model)
对于interleaving的offset定义有些复杂,定义如下: 1
2
3offset = mpu.get_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_rank() * (
args.num_layers // args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size) + \
(mpu.get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank() * self.num_layers)
mpu.get_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_rank() * (args.num_layers // args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size)表示先按大的虚拟组来做区分,然后在每个大虚拟组中再切分小块(chunk)。以layer_num=8, stage_num=2, virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size=2为例,大的虚拟组的偏移分别是0和4,这里的self.num_layers大小为2,
mpu.get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank()的值有0和1(stage为2),最终组合起来可能的值有0, 2, 4, 6。在使用offset求最终的layer编号时,也是跟之前非interleaving一样的方式。
1
2self.layers = torch.nn.ModuleList(
[build_layer(i + 1 + offset) for i in range(self.num_layers)])
最终device0对应的model有两个ModuleList,
分别是ModuleList[l0, l1]和ModuleList[l4, l5];device1对应的model也有两个ModuleList,分别是ModuleList[l2, l3]和ModuleList[l6, l7]
1
2device0(stage1) : {ModuleList[l0, l1], ModuleList[l4, l5]}
device1(stage2) : {ModuleList[l2, l3], ModuleList[l6, l7]}
2.5 forward_backward_pipelining_with_interleaving运行流程
在一开始跟without_interleaving情况一样,需要关闭自动的grad更新;同时由于存在多个model,这里要保存多个model的输入input_tensors和输出output_tensors。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7disable_grad_sync()
# Model chunk IDs with synchronized grads
synchronized_model_chunks = set()
input_tensors = [[] for _ in range(len(model))]
output_tensors = [[] for _ in range(len(model))]
如果是sequence并行的话,是从sequence维度对矩阵tensor进行切分为get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()份。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7if sequence_parallel:
seq_length, batch_size, hidden = tensor_shape
tensor_shape = (
seq_length // parallel_state.get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size(),
batch_size,
hidden,
)
warmup前计算每个device在warmup阶段要用到的microbatch数量num_warmup_microbatches。
*
首先计算总的total_num_microbatches,等于传入的microbatch和len(model)的乘积,如果virtual_stage=2的话,这里num_model_chunks值对应是2。
*
如果num_microbatches等于pipeline_parallel_size,并行方式跟GPipe中的思路一样,先全forward再走backward,在warmup阶段把所有的microbatch都训练完。
*
如果num_microbatches不等于pipeline_parallel_size,warmup的计算的单位按pipeline_parallel_size来进行,num_warmup_microbatches计算分为两部分,第一部分是在阶梯下降时每个device处理的microbatch个数正好错一个,对应rank号大小,用\(pipeline\_parallel\_size -
pipeline\_parallel\_rank - 1) * 2\)计算;
第二部分是等量增加的部分,用\((num\_model\_chunks - 1) *
pipeline\_parallel\_size\)来计算。示例如下图: 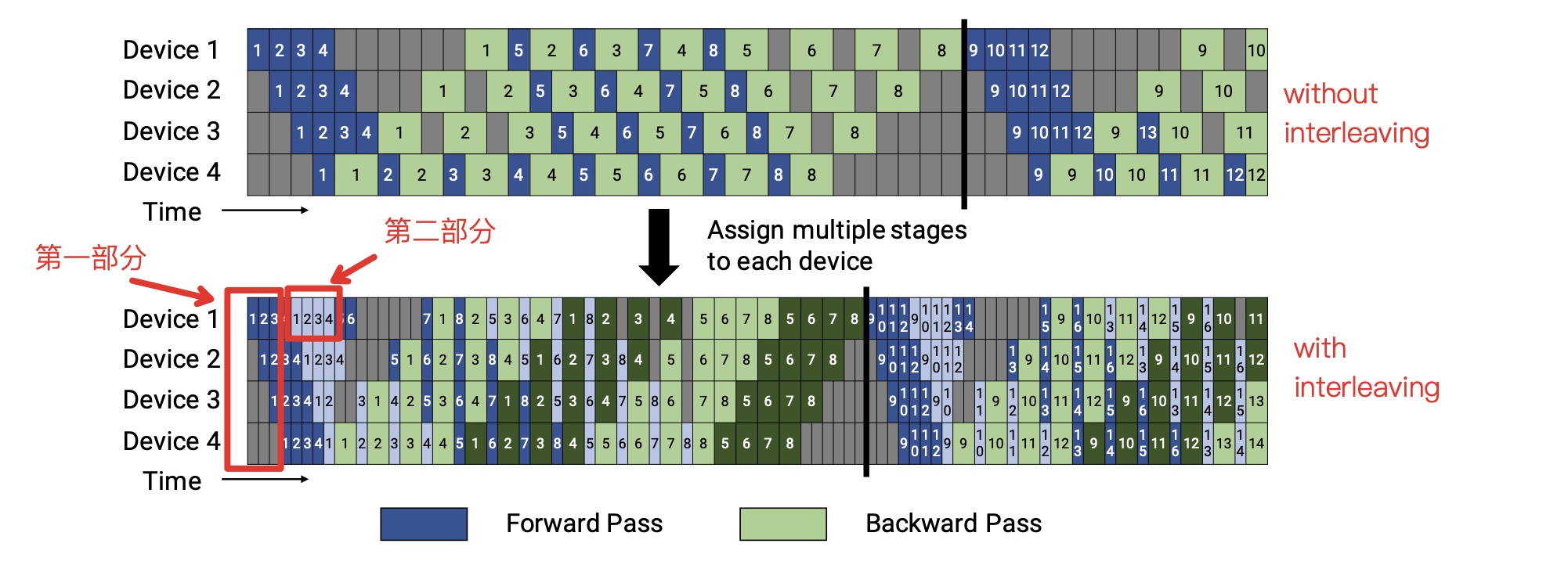 * 代码实现:
* 代码实现: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13# Compute number of warmup and remaining microbatches.
num_model_chunks = len(model)
total_num_microbatches = num_microbatches * num_model_chunks
......
if num_microbatches == pipeline_parallel_size:
num_warmup_microbatches = total_num_microbatches
all_warmup_microbatches = True
else:
num_warmup_microbatches = (pipeline_parallel_size - pipeline_parallel_rank - 1) * 2
num_warmup_microbatches += (num_model_chunks - 1) * pipeline_parallel_size
num_warmup_microbatches = min(num_warmup_microbatches, total_num_microbatches)
num_microbatches_remaining = total_num_microbatches - num_warmup_microbatches
在这里还实现了几个辅助函数分别是: 1.
get_model_chunk_id(microbatch_id, forward):
获取microbatch_id对应的model_chunk_id 2.
is_first_microbatch_for_model_chunk(microbatch_id: int):
microbatch_id是否是model chunk中的第一个microbatch 3.
is_last_microbatch_for_model_chunk(microbatch_id: int):
microbatch_id是否是model chunk中的最后一个microbatch 4.
forward_step_helper(microbatch_id, checkpoint_activations_microbatch):
执行microbatch_id对应的前向 5.
backward_step_helper(microbatch_id):
执行microbatch_id对应的反向
以interleaving 1F1B稳定状态为例,对应的流程如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35# 遍历处理每个个micro
for k in range(num_microbatches_remaining):
......
if config.overlap_p2p_comm:
......
else: # no p2p overlap
# 先进行1 forward,forward_k是microbatch_id
# 跟without-interleaving不同的是forward中会跟据microbatch_id计算model_chunk_id,跟据model_chunk_id运行对应的forward_step
output_tensor = forward_step_helper(forward_k, checkpoint_activations_microbatch)
# 再进行1 backward, 类似forward
backward_k = k
input_tensor_grad = backward_step_helper(backward_k)
......
# 计算完前向和后向,跟前向和后向的rank结点进行通信
input_tensor, output_tensor_grad = \
p2p_communication.send_forward_backward_recv_forward_backward(
output_tensor, input_tensor_grad,
recv_prev=recv_prev, recv_next=recv_next,
tensor_shape=tensor_shape, config=config)
deallocate_output_tensor(output_tensor, config.deallocate_pipeline_outputs)
# 在一批microbatch训练结束后,进行grad的同步操作
enable_grad_sync()
if config.grad_sync_func is not None:
params = []
for model_chunk_id in range(num_model_chunks):
if model_chunk_id not in synchronized_model_chunks:
params.extend(model[model_chunk_id].parameters())
synchronized_model_chunks.add(model_chunk_id)
if params:
config.grad_sync_func(params)
return forward_data_store
注意interleaving目前的一些限制: * 不支持encoder-decoder类的模型 *
如果len(model) > 1或mpu.get_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size() > 1时,只支持args.DDP_impl='local'
* 要求num_microbatches % pipeline_parallel_size == 0